There can be a lot of new and confusing terms when you first begin to learn about Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). If you’re scrolling /BPD on Reddit or browsing through tumblr, it can be full of terms like pwBPD and FP - and no explanation of what they mean!
That’s why we’ve created this helpful little glossary of BPD terms that will get you up to speed quickly. Like many of our articles, we intend to expand and update this list of terms over time. We welcome questions or requests in the comments about any terms that you’d like to see added.
With that said, here is our ever-growing glossary of BPD terms!

BPD: A simple one here but BPD stands for Borderline Personality Disorder. The acronym is sometimes mistaken for Bipolar Disorder.
Catastrophizing: Catastrophizing is when a person fixates on the worst outcome possible in a situation and expects it to be likely to happen, leading to increased anxiety and stress. Catastrophizing is common among people with BPD.
Cluster B: There are three recognized clusters of personality disorders. Cluster B refers to personality disorders that are seen as involving dramatic/erratic behavior. This is the cluster that BPD belongs to, along with Narcissistic Personality Disorder, Antisocial Personality Disorder, and Histrionic Personality Disorder.
DBT: DBT stands for Dialectical Behavior Therapy. Research has found this to be the most successful form of therapy used to treat BPD. For more about DBT, please read our article: Dialectical Behavior Therapy and Borderline Personality Disorder
Depersonalization: Depersonalization is a kind of dissociation in which an individual disconnects from reality and feels as if they’re seeing themselves from outside their body. It’s as if they’re a viewer of their life rather than an active participant.
Derealization: Derealization is a type of dissociation and is the feeling of being disconnected from your environment. During derealization, you may feel like nothing is real or, that you’re in a dream.
Discouraged BPD: Also known as Quiet BPD. Discouraged BPD is one of the four subtypes of BPD. People with Discouraged BPD tend to internalize their emotional turmoil. For more on Discouraged BPD, read our article: What is Discouraged BPD?
Dissociation: Dissociation is a process whereby a person disconnects from reality as a coping mechanism in times of heightened stress or emotional turmoil. Depersonalization and derealization are the two most common forms of dissociation.
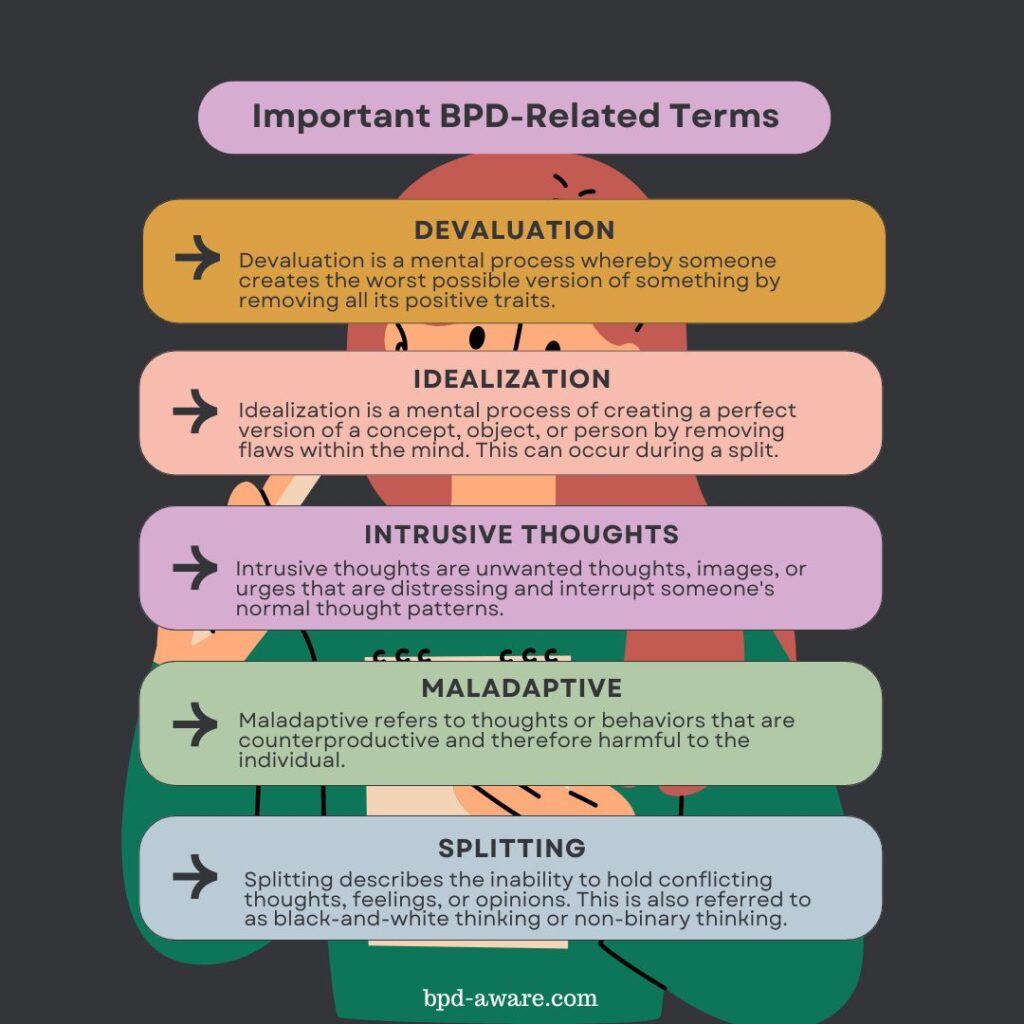
Devaluation: Devaluation is a mental process whereby someone creates the worst possible version of a concept, object, or person by removing all their positive traits. This is commonly seen during splitting.
Emotional Permanence: Emotional permanence refers to the ability to understand that an emotional connection still exists with someone even when they’re not physically present. Some people with BPD struggle with emotional permanence due to abandonment fears.
EUPD: EUPD is an acronym that stands for Emotionally Unstable Personality Disorder. This is an alternate name for BPD that is more commonly used in Europe. For more about EUPD and its uses, you can read our article: What is EUPD?
FP: FP is an acronym for Favorite Person. Some people with BPD become hyper-attached to one person and this is known as an FP. For more about the Favorite Person Phenomenon you can read our article: What Does FP Mean in BPD Culture?
Hoovering: Hoovering is a form of manipulation used to draw someone back into a toxic relationship. This can involve tactics such as flattery, gifts, empty promises, or threats. Some people with BPD may employ these tactics, while others with BPD won’t. People with BPD are also particularly prone to hoovering due to their fear of abandonment. You can find out more about this by reading our article: BPD and Hoovering
Idealization: Idealization is a mental process of creating a perfect version of a concept, object, or person by removing flaws within the mind. This can occur during a split.
Impulsive BPD: One of the four subtypes of BPD, Impulsive BPD is characterized by frequent bouts of reckless behavior such as substance abuse, dangerous driving, or spending large amounts of money. For more on Impulsive BPD, please read our article: What is Impulsive BPD?
Intrusive Thoughts: Intrusive thoughts are unwanted thoughts, images, or urges that are distressing and interrupt someone’s normal thought patterns. For example, someone might have an intrusive thought about dunking their hand in boiling water while cooking.
Maladaptive: Maladaptive refers to thoughts or behaviors that are counterproductive and therefore harmful to the individual. For example, someone might avoid socializing because they’re scared they will be rejected. This only leads to isolation and is likely to exacerbate mental health issues.
Masking: Masking is a process in which a neurodivergent individual attempts to repress or hide their genuine thoughts and behaviors in an effort to conform to social expectations.
Mindfulness: Mindfulness is derived from the Buddhist practice of maintaining a non-judgemental awareness of the present moment. By staying in the moment, you can remove the baggage of the past and concerns about the future. Mindfulness is taught as part of DBT and is a useful skill for people with BPD to learn.
Neurodivergent/Neuroatypical: Both these terms mean the same thing and refer to someone whose neurological development and functioning differs from typical cognitive norms. Someone with BPD would be considered neurodivergent.
Neurotypical: Neurotypical (not to be mistaken with neuroatypical) refers to people whose cognitive development and functioning follow the typical social norms.
NPD: NPD stands for Narcissistic Personality Disorder, which is the Cluster B of personality disorders along with BPD. People with NPD often have little empathy, an inflated sense of importance, and a need for excessing attention. It’s not uncommon for people with BPD to also have NPD. Because of their relative symptoms, relationships between someone with BPD and someone with NPD can be particularly toxic. For more about NPD, please read our article: The Relationship Between Borderline Personality Disorder and Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Petulant BPD: Petulant BPD is one of the four subtypes of BPD. It’s characterized by strong feelings of jealousy and petulant behavior such as passive-aggressiveness. For more on Petulant BPD, read our article: What is Petulant BPD?
PwBPD: pwBPD stands for a person with BPD. It’s a shorthand that you’ll often see on social media.
Rumination: Rumination is repetitive and persistent thinking about distressing situations or thoughts. Thought patterns like this often exacerbate emotional turmoil and anxiety. Rumination is common among people with BPD.
Schema Therapy: Schema Therapy is a popular form of therapy used to treat BPD. It aims to help people identify and alter maladaptive thoughts and behaviors to improve emotional regulation and relationships.
Self-Destructive BPD: Self-Destructive BPD is one of the four subtypes of BPD. It’s characterized by a strong desire to destroy the self. This is evidenced by self-harm, suicidal behavior, severe depression, and self-hatred. To discover more about Self-Destructive BPD, read our article here: What is Self-Destructive BPD?
Split/Splitting: Splitting describes the inability to hold conflicting thoughts, feelings, or opinions. This is also referred to as black-and-white thinking or non-binary thinking. For example, someone splitting might think that one person is perfect while someone else is worthless. People with BPD are highly prone to splitting. For more on splitting, please read our article: What is Splitting in Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)?
Stigma: Stigma refers to the negative attitudes and beliefs that lead to discrimination and marginalization against people based on characteristics or conditions. There is still a lot of stigma surrounding mental health and BPD.
Trigger: A trigger is a stimulus or event that causes an intense emotional reaction. Triggers vary from person to person and typically link to past traumatic experiences.
Wise Mind: Wise Mind is a balanced state where emotional and rational thought are allowed to co-exist. Wise Mind allows for clear thinking and better decision making. For more on Wise Mind, please read our article: DBT Skills: Wise Mind